Aluminum Truss Maintenance Checklist to Extend Lifespan and Reduce Waste
Identifying Dents, Bends, and Cracks Before and After Use
Scan truss surfaces under bright, angled lighting to reveal surface deformities. Focus on:
- High-stress junctions: The majority of truss failures originate at connection points
- Recessed areas: Hidden bends in hollow sections often go unnoticed until load testing
- Diagonal braces: Check for warping caused by uneven weight distribution
Post-event inspections should verify no new damage occurred during use. Document findings immediately using geo-tagged photos.
Detecting Micro-Cracks at Stress Points Using Visual and Tactile Methods
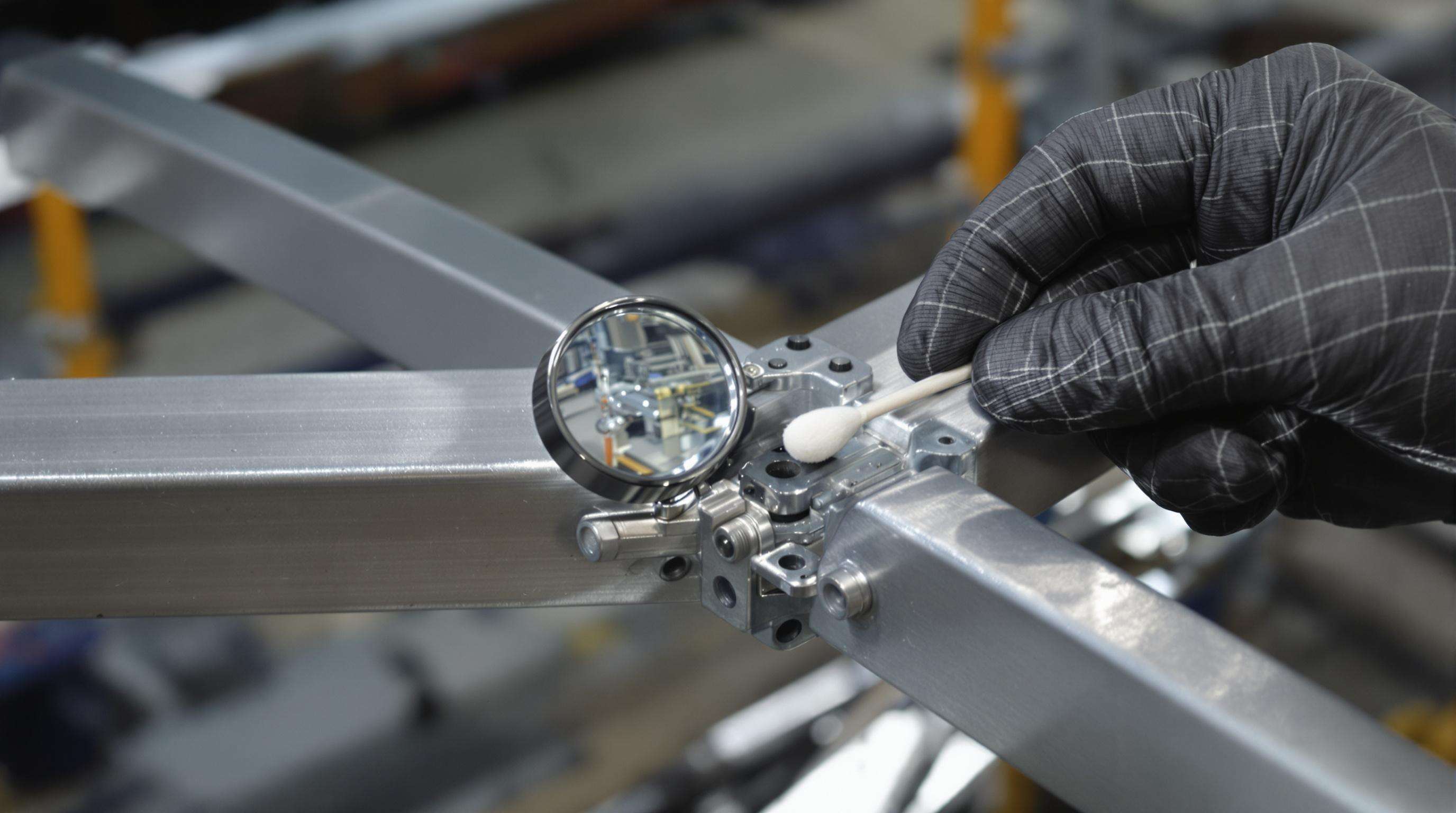

Micro-cracks measuring <0.3mm often evade visual detection but significantly compromise structural integrity. Combine these techniques:
- Coin tap testing: A sharp metallic ring indicates solid material, while dull sounds suggest subsurface cracks
- Magnified inspection: Use 10x loupes on weld seams and machined edges
- Thread tracing: Drag cotton swabs along surfaces – snags reveal crack locations
Conducting Deep Inspections and Structural Integrity Tests
Professional evaluations every 400 operating hours should include:
- Non-destructive testing (NDT): Dye penetrant exams uncover hairline fractures
- Load verification: Apply 110% of rated capacity for 60 minutes while monitoring deflection
- Ultrasonic thickness measurements: Identify internal corrosion reducing wall strength
Using Checklists and Digital Logging for Consistent Field Inspections
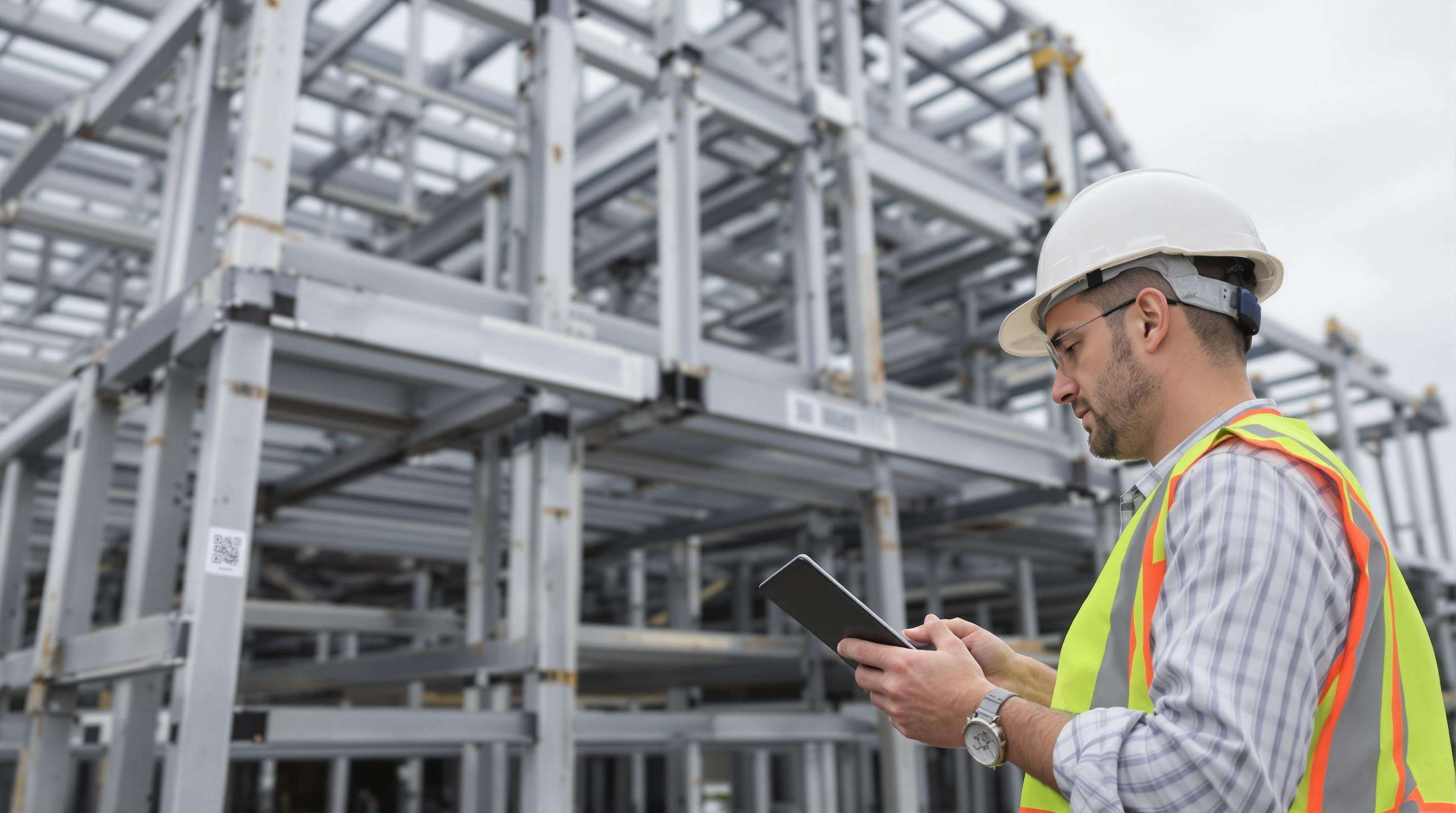

Standardized checklists improve defect detection rates by 41% compared to ad-hoc methods. Modern solutions combine:
- QR code tracking: Scan components to access maintenance histories instantly
- Cloud-based reporting: Auto-flag components exceeding damage thresholds
- Condition scoring: Rate sections on a 1-5 scale to prioritize repairs
Maintenance logs linked to serial numbers create auditable safety records, reducing liability risks in case of incidents.
Cleaning and Corrosion Prevention for Aluminum Truss Systems
Safe Cleaning Methods Using Mild Soap and Non-Abrasive Tools
Preserve aluminum truss surfaces by cleaning with pH-neutral soap and warm water after every use. Microfibre cloths or soft-bristle brushes prevent scratches while removing dirt and grease. For stubborn residues, apply isopropyl alcohol (70% concentration) with a cotton pad, then rinse immediately.
Key Practices:
- Avoid steel wool or abrasive pads that compromise the oxide layer
- Dry components thoroughly with lint-free towels
- Never use high-pressure washers exceeding 50 PSI
Removing Corrosive Residues From Transport and Outdoor Exposure
After coastal events or road transport, treat surfaces with a vinegar-water solution (1:3 ratio) to neutralize salt deposits. For pesticide or fertilizer contamination, rinse with distilled water within 4 hours of exposure.
Protecting Trusses in Humid or Coastal Environments
Store aluminum trusses in climate-controlled environments (<60% humidity). In unavoidable damp conditions:
- Install silica gel packs (1,500g per 10m³) in storage containers
- Apply corrosion-inhibiting sprays quarterly
- Inspect load-bearing joints weekly for "white rust" during rainy seasons
Enhancing Durability With Powder Coating and Anodizing
Electrostatic powder coating adds a 60–120 ¼m protective layer, while anodizing creates a 25 ¼m oxide barrier that withstands UV degradation. For mixed-material systems, prioritize:
- Class III anodizing for coastal deployments
- Epoxy-primed powder coats on weld zones
- Re-coating intervals every 5–7 years for permanent installations
Proper Storage and Handling to Prevent Environmental and Mechanical Damage
Storing aluminum trusses to avoid moisture, deformation, and improper stacking
| Storage Factor | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Environment | Maintain 60% relative humidity |
| Stacking Method | Use pallets or racks |
| Moisture Protection | Apply silica gel packs in humid climates |
Safe handling practices: avoiding dragging, dropping, and overloading
- Lifting Protocol: Use forklifts or padded slings rated for 1.5x truss weight
- Movement Guidelines: Never drag components
- Load Management: Distribute weight evenly across connection points
Training crews on load limits and structural stress points
Field teams require quarterly drills on:
- Calculating dynamic vs. static load limits
- Identifying micro-cracks near welded joints
- Using torque wrenches for connection integrity
Minimizing onsite damage during transport and installation
- Wrap truss ends with 3mm neoprene sleeves
- Conduct pre-installation inspections for:
- Bent connector plates
- Thread wear on adjustable leg screws
- Secure all joints with secondary locking pins in high-wind conditions
Maintaining Fasteners and Joints for Long-Term Structural Integrity
Inspecting, Tightening, and Lubricating Bolts, Pins, and Clamps
| Component | Inspection Frequency | Torque Range (Nm) | Lubricant Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolts | Every 5 setups | 20–35 | Dry-film silicone |
| Pins | Every 10 setups | N/A | Graphite spray |
| Clamps | Every 3 setups | 15–25 | Anti-seize compound |
Preventing Loosening Due to Vibration in Aluminum Truss Connections
Mitigate risks with:
- Lock washers or nylon-insert nuts
- Thread-locking adhesives
- Post-event "re-torque" checks after 24–48 hours of use
Replacing Worn or Damaged Components to Ensure Safety and Performance
Use dye penetrant kits during annual deep inspections to identify hidden flaws. A single compromised bolt can reduce joint strength by 40%.
Best Practices for Joint Maintenance in Modular Metal Systems
- Document every inspection and repair
- Train crews to recognize early wear patterns
- Retire components after exceeding 80% of service cycles
Implementing a Routine Maintenance Schedule for Optimal Performance
Developing a preventative maintenance plan with scheduled inspection intervals
Operators should conduct:
- Daily visual checks
- Weekly load-bearing assessments
- Monthly professional inspections
- Annual load-test recertification
Integrating maintenance logs and professional audits into operations
Digital maintenance tracking systems enable:
- Time-stamped repair histories
- Photographic documentation
- Automated reminders
Extending aluminum truss lifespan through consistent servicing
Critical practices include:
- Lubrication schedules for moving components
- Wear pattern analysis
- Surface renewal protocols for anodized finishes
Reducing waste and costs with proactive maintenance strategies
Implement:
- Spare critical parts inventories
- Predictive wear modeling
- Scrap metal recycling programs
FAQs
Why is it important to inspect aluminum trusses regularly?
Regular inspections are crucial to detect structural defects early, prevent failures, and ensure the safety and longevity of truss systems.
How can micro-cracks be detected in aluminum trusses?
Micro-cracks can be detected using coin tap testing, magnified inspection, and thread tracing techniques.
What are the best practices for cleaning aluminum truss systems?
The best practices include using mild soap, non-abrasive tools, avoiding high-pressure washers, and drying components thoroughly after cleaning.
How can corrosion be prevented in aluminum trusses?
Corrosion can be prevented through safe storage, protective coatings, climate-controlled environments, and regular inspections.
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
The Application Scenarios Of Lighting Hooks And Trusses
2023-12-14
-
Market Analysis Of Lighting Hooks And Trusses
2023-12-14
-
The Essence Of Lighting Hooks And Trusses
2023-12-14
-
An In-Depth Look At Lamp Hooks And Truss Products
2023-12-14
-
Light Hooks And Truss Products: A Niche But Vital Industry
2023-12-14

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 LT
LT
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 IS
IS
 MK
MK
 EU
EU
 KA
KA